Emerson’s Cheng Vue shared tips for getting more insights from a Rosemount temperature transmitter. Here’s his presentation’s abstract:
Your installed temperature transmitter has features and diagnostics integral to its basic design that can be used to track, mitigate or diagnose process and device abnormalities. These features are fundamental to helping you understand your process variables. Do you know what these features are and how to use them? Discover how to utilize your Rosemount Temperature Transmitters to their fullest abilities, and you can be sure to get the most out of your Single and High Density Temperature Measurement Points!
Cheng opened noting some of the issues that can occur with temperature measurements. Problems with the temperature sensor and associated wiring can occur. Electromagnetic interference can impact the signal. Information within the transmitter can be used to optimize the process.
Temperature sensors and sensor wiring are very susceptible to failure from interface with the process, including temperature fluctuations and exposure to moisture and vibration.
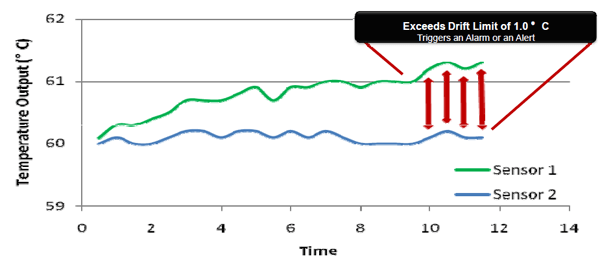
One capability to prevent sensor and sensor wiring problems is Hot Backup, which provides a constant Primary Variable despite a sensor failure. For inaccuracies due to sensor drift where two temperature sensors are installed on a critical process, they both must be giving accurate readings. The sensor drift alert helps track the reliability of 2 sensor measurements.
For thermocouple temperature sensors typically installed in high temperature processes and ones expensive to shutdown, the thermocouple degradation diagnostic can detect and alert on early problems.
 For the second class of issues, electromagnetic interference (EMI), ambient noise can affect measurement accuracy. Temperature sensor wiring can act as an antenna for EMI from transient electrical noise and AC power noise. Open sensor holdoff helps avoid high voltage transient noise, such as lightning, that cause open sensor alarms.
For the second class of issues, electromagnetic interference (EMI), ambient noise can affect measurement accuracy. Temperature sensor wiring can act as an antenna for EMI from transient electrical noise and AC power noise. Open sensor holdoff helps avoid high voltage transient noise, such as lightning, that cause open sensor alarms.
For intermittent temperature readings, where the transmitter is reporting extreme temperature fluctuations on a high vibration or high noise installation, an intermittent sensor detect diagnostic can be used. And for AC power noise, a line voltage filter is available to mitigate this 50 or 60Hz noise.
Process optimization is the final area where diagnostics and capabilities are available. To assist with troubleshooting which includes diagnosing errant and reoccurring alarms, verify correct installations, find temperature-related quality issues and optimize measurement accuracy. Transmitter-sensor matching addresses insufficient measurement accuracy.
Configurable process alerts helps spot temperature fluctuations beyond configured values. These capabilities in the Rosemount temperature transmitters can be used to track, mitigate or diagnose process and device abnormalities.
You can connect and interact with other temperature measurement experts in the Temperature track of the Emerson Exchange 365 community.