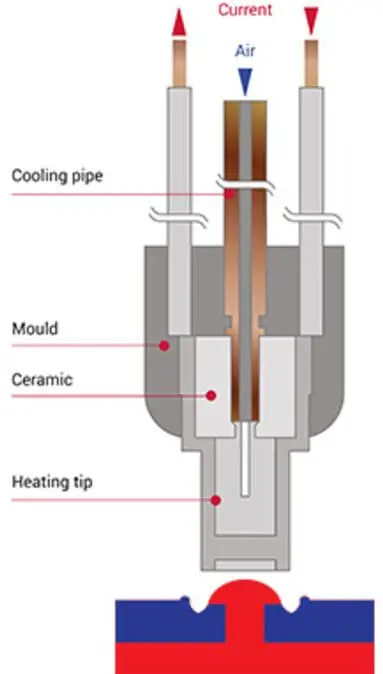
Heat staking also known as thermoplastic staking is the process of joining two dissimilar materials together. Some typical applications for heat staking include polymer to polymer to other materials, flat head tip welding, sealing holes, embedding parts, polymer to mesh, breathable membrane, rim swaging, bonding, polymer to polymer welding, and polymer to polymer.
In a Medical Device and Diagnostic Industry (MD+DI) article, Advanced Technology for Plastics Staking and Swaging, Emerson’s Priyank Kishor describes a technology innovation, pulse staking. Pulse staking uses local heating and cooling to raise the temperature of plastic components and allow plastic reforming to be carried out.
Priyank opens describing the advantages of thermoplastic stakes and swages.
Permanent and strong thermoplastic stakes or swages can be made quickly and at relatively low cost, without the need for processes involving labor-intensive mechanical fastening or expensive adhesive-fastening processes.
Thermal and ultrasonic staking have been the traditional technologies to produce these stakes. Traditional thermal staking:
…or swaging uses a continuously heated tip that is moved into contact with plastic, where it melts the plastic and forms it according to the shape of the tip.
Ultrasonic:
…swaging or staking employs vibratory energy, also applied through metal tooling, to create frictional heat that is used to melt and form plastic stakes or swages.
…localized, changeable temperatures during the plastic-forming process. Each tip combines an electrical heating element with a compressed-air cooling system. This design instantaneously heats or cools the tip by applying “pulses” of heating or cooling that precisely manage the temperature of the plastic.
This pulse staking technology advancement:
…enables them to form plastic stakes and swages with consistent strength and a high-quality finish, even when these must be made in close proximity to other plastics…
Priyank highlights the biggest advantage in its:
…ability to perform in very challenging, high-value staking or swaging applications that were either very difficult or impossible to complete with other approaches.
Some of these challenging applications include complex 3-D parts, innovative advanced materials, and fragile and heat-sensitive components such as printed circuit boards.
Read the article for more on how pulse staking technology addresses challenging applications and provides greater aesthetics, consistency and quality than other staking and swaging technologies.
Visit the Heat Staking section on Emerson.com for more on Branson heat staking products and how it can address challenges found in industries that require sensitive plastic parts to be joined, such as Automotive, Electronics and Medical.